Turner Syndrome Heart Defects
Turner syndrome heart defects. Here the cardiovascular complications of Turner syndrome are reviewed. Boys have one X and one Y. Various studies using different imaging techniques have demonstrated that 25-50 of patients with TS have some form of congenital cardiovascular defect.
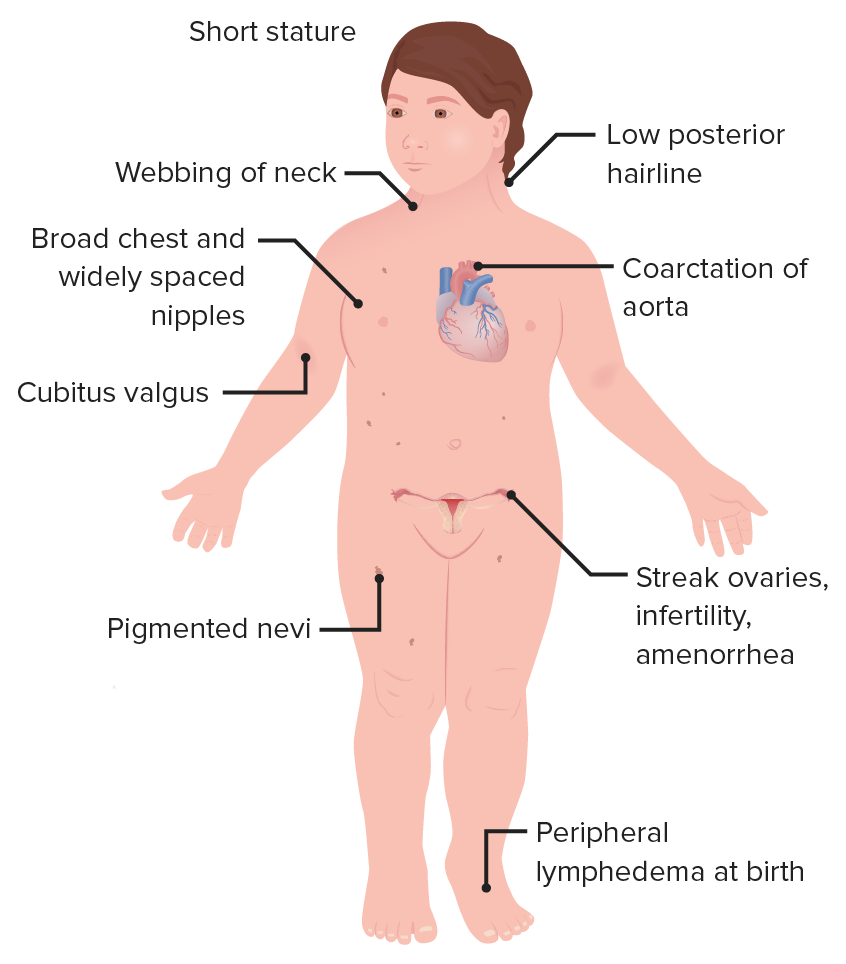
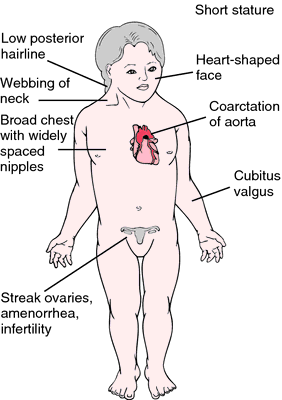
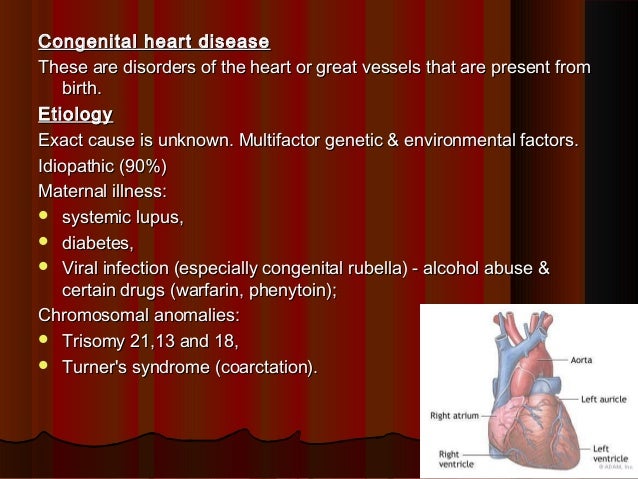
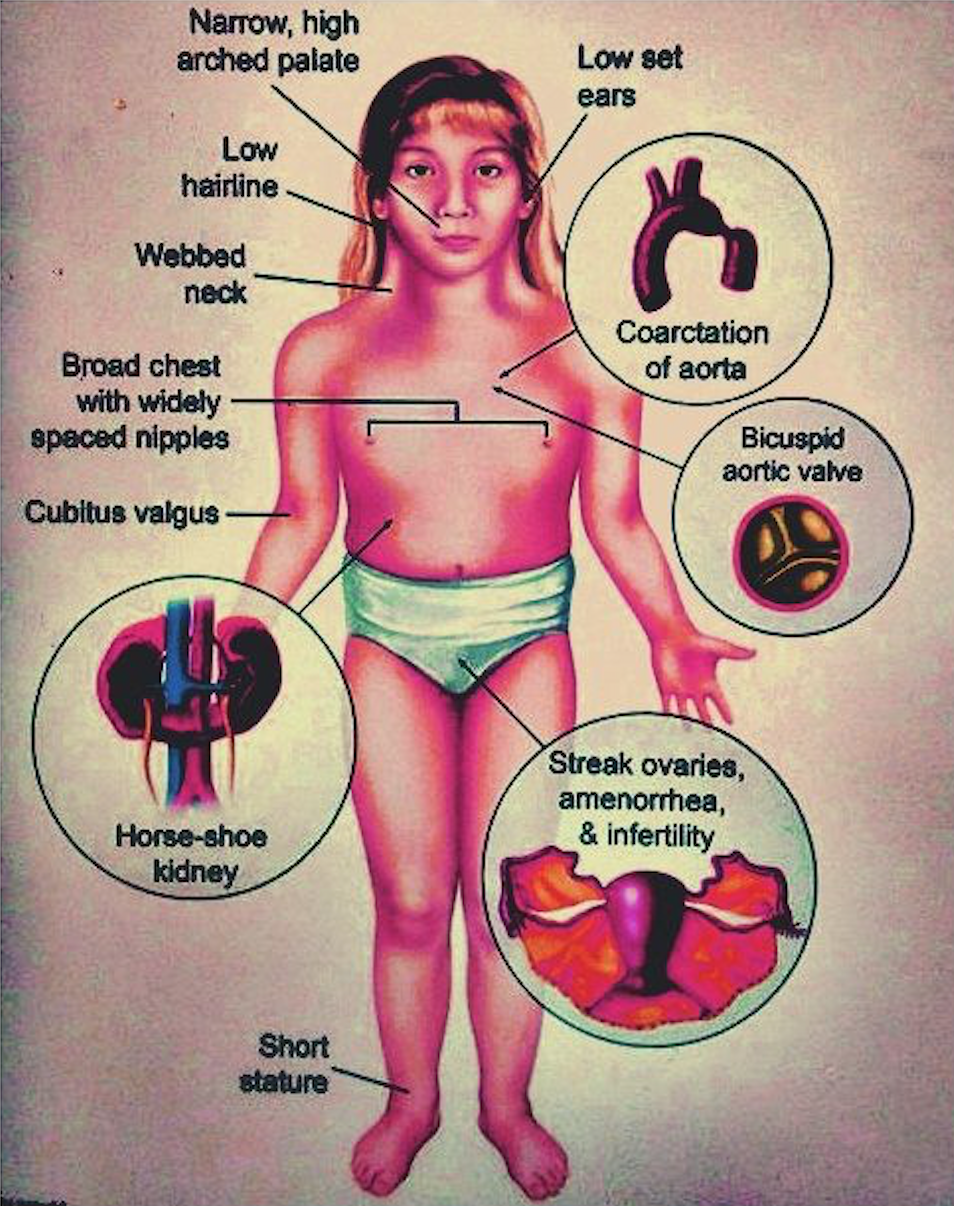
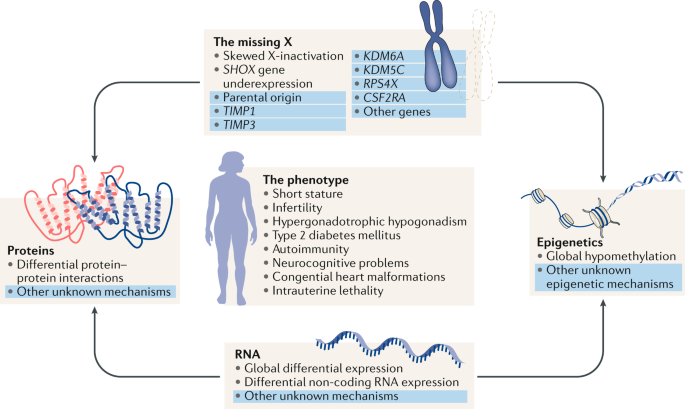
The occurrence of cardiac malformations in Turner syndrome gonadal dysgenesis with sex chromosome aneuploidy has long been recognized. Turner syndrome is a genetic defect or a chromosomal disorder that mainly affects females around the world. Turner syndrome is associated with short stature delayed puberty ovarian dysgenesis hypergonadotropic hypogonadism infertility congenital malformations of the heart endocrine disorders such as type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis and autoimmune disorders.
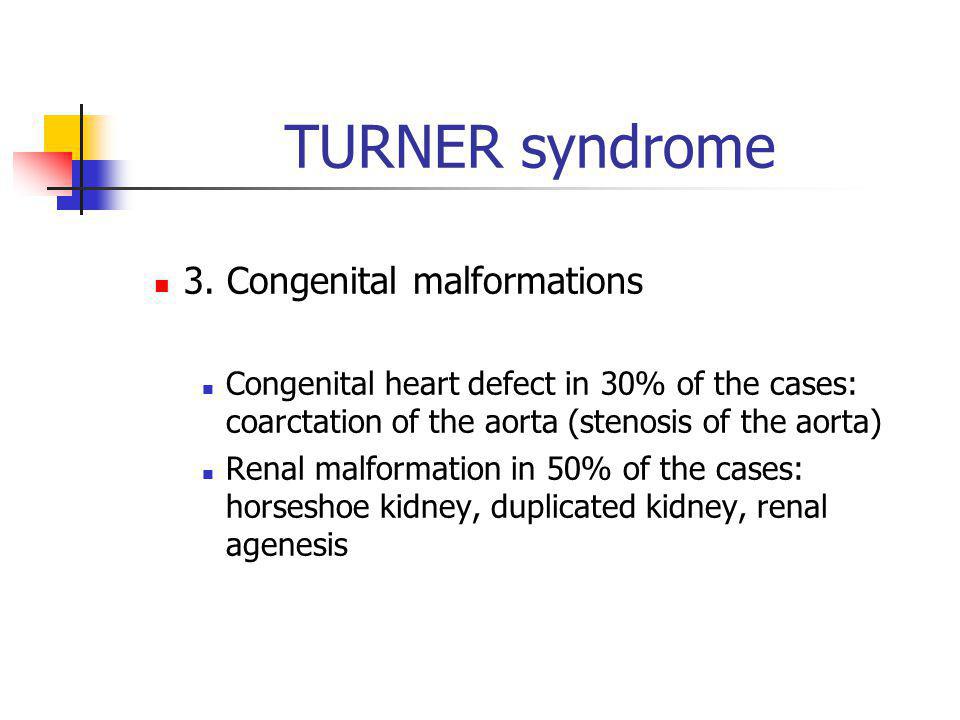
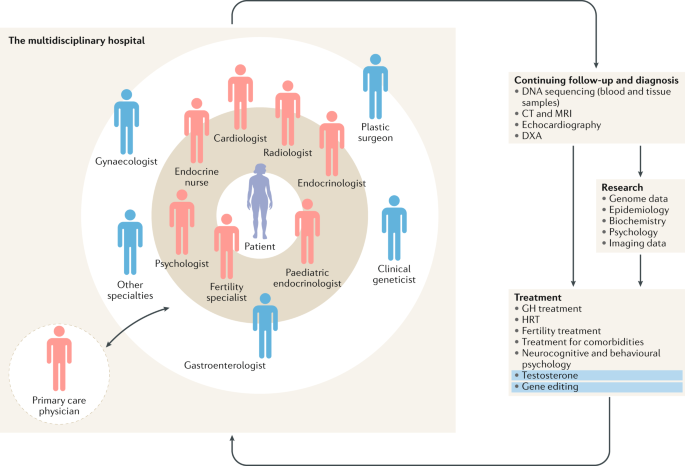
In a recent query of the Texas Birth Defect registry 11 patients were identified. The poor prognostic association of Turners syndrome and hypoplastic left heart syndrome has been well described Table 2. It is well known that patients with Turners syndrome have a high risk for cardiovascular malformations.
Des anomalies cardiaques congénitales sont décrites chez environ un tiers des patientes. The prevalence of cardiovascular malformations in these studies ranged from 17 to 26. It affects only girls and women because it is caused by a missing or incomplete X chromosome normally girls have two X chromosomes.
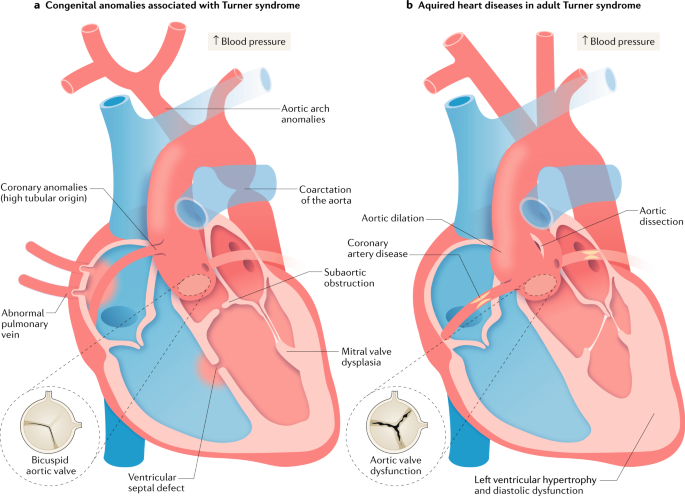
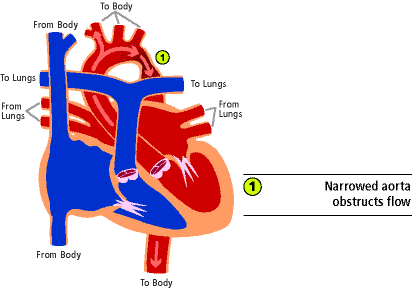
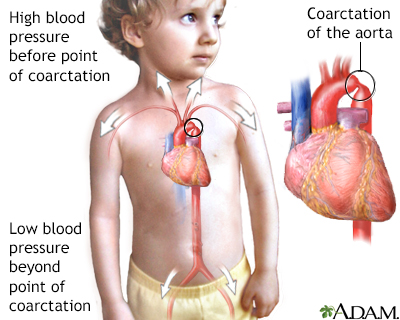
Defects in the main blood vessel leading out of the heart aorta increase the risk of a tear in the inner layer of the aorta aortic dissection. The Heart and Turner Syndrome Cardiovascular abnormalities are one of the most common complications in girls and women with Turner Syndrome TS Congenital heart disease occurs in up to 50 of individuals with TS and is more common in those with a 45X karyotype. CHD in Turners syndrome includes varying degrees of left heart obstruction.
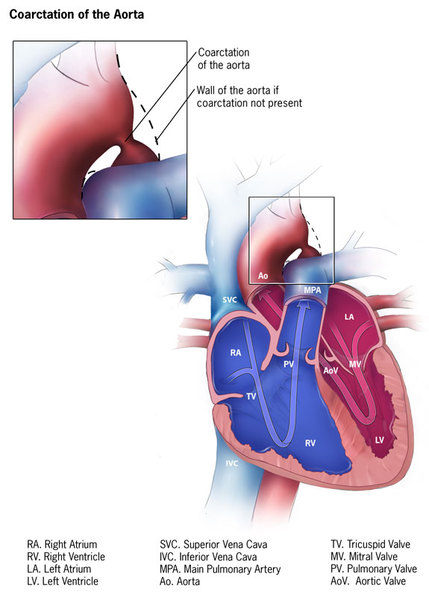
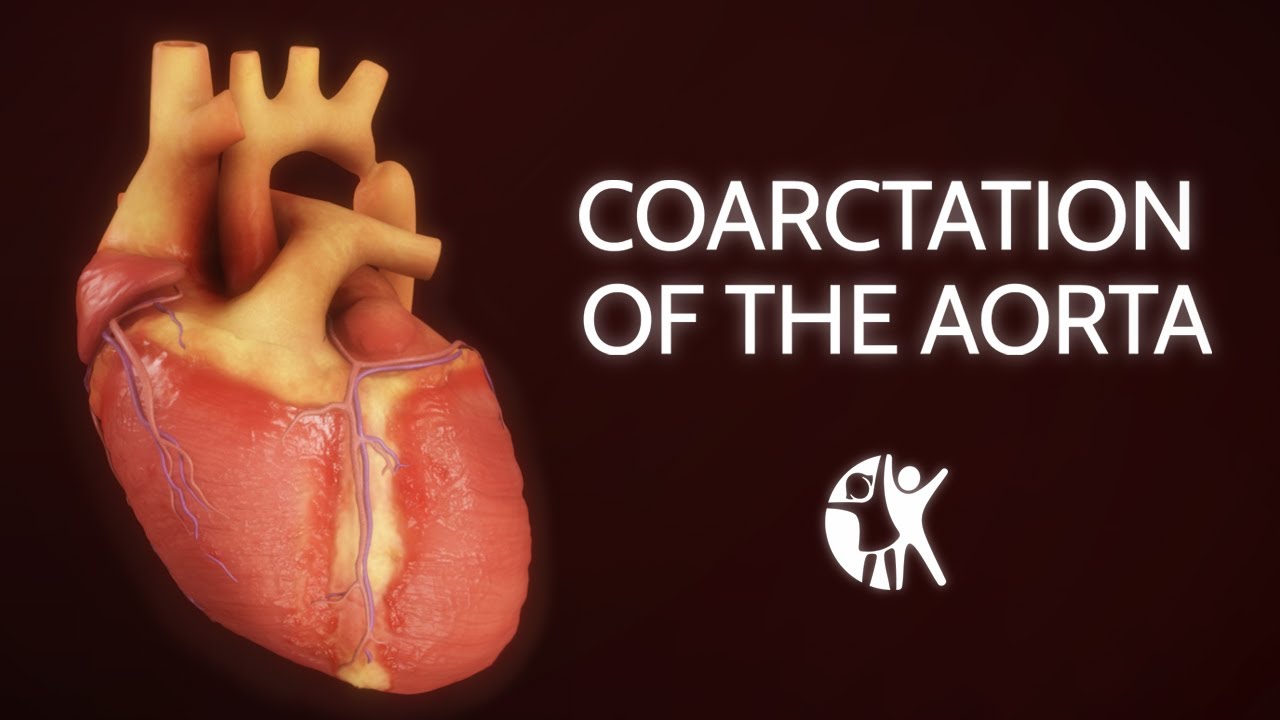
1 The most common heart defects are coarctation of the aorta Coarct and bicuspid aortic valve BAV. Heart disease is very common in Turner syndrome. One third to one half of individuals with Turner syndrome are born with a heart defect such as a narrowing of the large artery leaving the heart coarctation of the aorta or abnormalities of the valve that connects the aorta with the heart the aortic valve.
The risk of congenital heart defects such as bicuspid aortic valves aortic coarctation. Many advancements in the treatment of the disease have been made.
The condition is rare only affecting about 1 in 2500 female births worldwide.
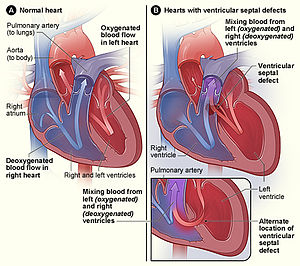
Many advancements in the treatment of the disease have been made. Complications associated with these heart defects can be life-threatening. It is well known that patients with Turners syndrome have a high risk for cardiovascular malformations. Typically women suffering from this disorder exhibit short stature learning difficulties and emotional distress. Dans le syndrome de Turner les complications cardiovasculaires sont les principales responsables dune surmortalité précoce avec une espérance de vie qui pourrait être réduite de plus de dix ans. Bicuspid aortic valve is common and many have left-sided heart obstructive disease of varying severity from hypoplastic left-sided heart syndrome to minimal aortic stenosis or coarctation of the aorta. Various studies using different imaging techniques have demonstrated that 25-50 of patients with TS have some form of congenital cardiovascular defect. It affects only girls and women because it is caused by a missing or incomplete X chromosome normally girls have two X chromosomes. Here the cardiovascular complications of Turner syndrome are reviewed.
Defects in the main blood vessel leading out of the heart aorta increase the risk of a tear in the inner layer of the aorta aortic dissection. The Heart and Turner Syndrome Cardiovascular abnormalities are one of the most common complications in girls and women with Turner Syndrome TS Congenital heart disease occurs in up to 50 of individuals with TS and is more common in those with a 45X karyotype. 1 The most common heart defects are coarctation of the aorta Coarct and bicuspid aortic valve BAV. This is because it involves a complete or partial loss of the second sex chromosome in some or all the cells. Bicuspid aortic valve is common and many have left-sided heart obstructive disease of varying severity from hypoplastic left-sided heart syndrome to minimal aortic stenosis or coarctation of the aorta. Left-sided heart defects are most common with frequencies of. The prevalence of cardiovascular malformations in these studies ranged from 17 to 26.































Post a Comment for "Turner Syndrome Heart Defects"