Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Mri
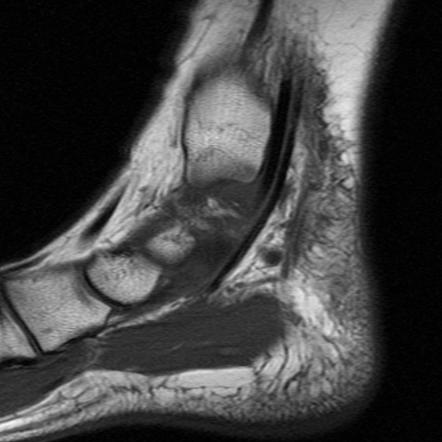
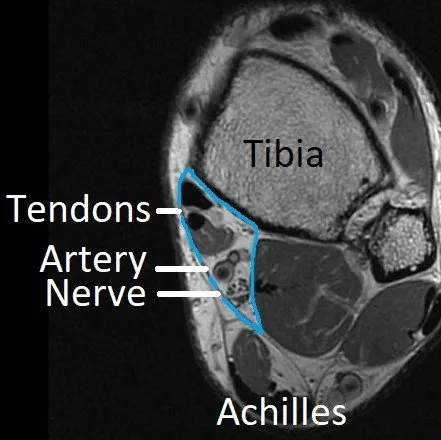
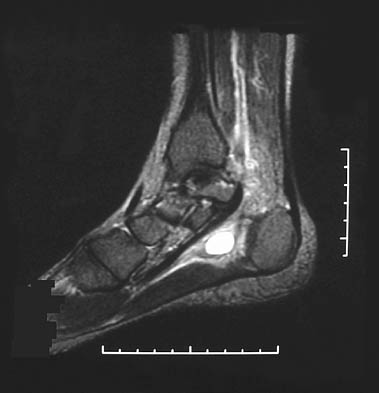
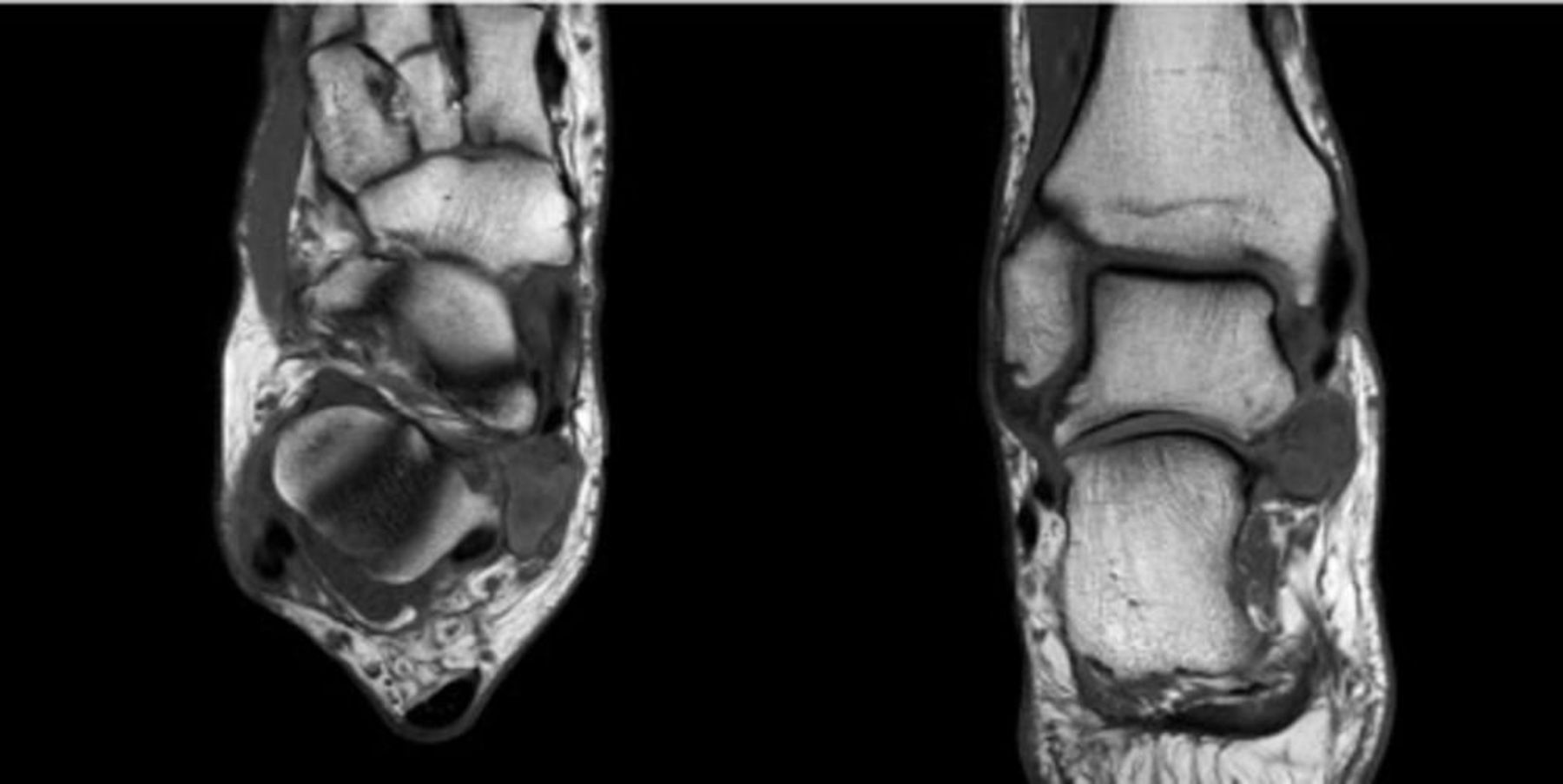
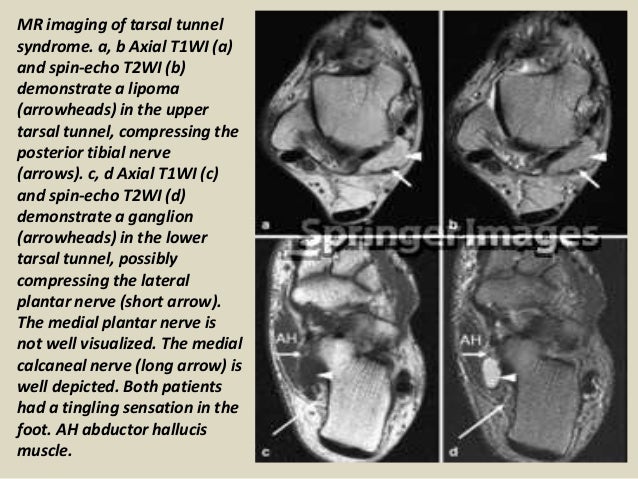
Tarsal tunnel syndrome mri. Tarsal tunnel syndrome TTS is caused by compression of the tibial nerve or any of its three terminal branches under the flexor retinaculum. The tarsal tunnel is divided by fibrous septae joining the flexor retinaculum to the calcaneus forming four separate compartments - one for each of the tendons and one for the neurovascular bundle 1-3. Ab Axial T1WI a and spin-echo T2WI b demonstrate a lipoma arrowheads in the upper tarsal tunnel compressing the posterior tibial nerve arrows.
MR imaging can accurately depict the contents of the tarsal tunnel and the courses of the terminal branches of the posterior tibial nerve. MR imaging may also be used to follow up non-surgical causes of tarsal tunnel syndrome such as tenosynovitis. MRI is NOT a valuable tool for this as most of the time especially in the early stages of the problem there are no MRI findings It is a clinical diagnosis meaning it has to diagnosed by a physician who has training in peripheral nerve problems like Dr.
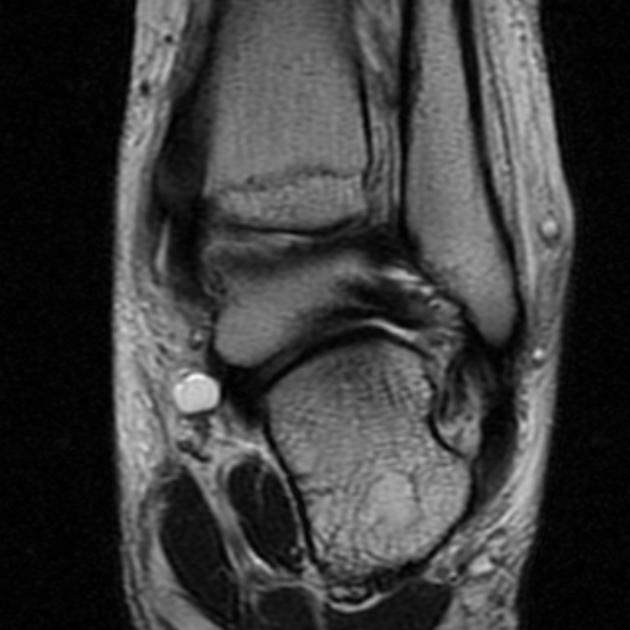
It is continuous distally with plantar aponeurosis and proximally with the deep fascia of the leg. MR imaging of tarsal tunnel syndrome. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome MRI Test MRI is ideally suited for evaluation of the tarsal tunnel due to its excellent soft tissue contrast ability to demonstrate neurovascular and musculotendinous structures and sensitivity to soft tissue pathology.
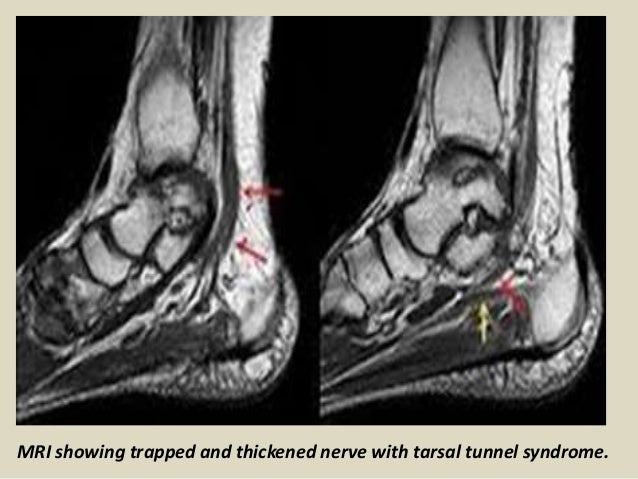
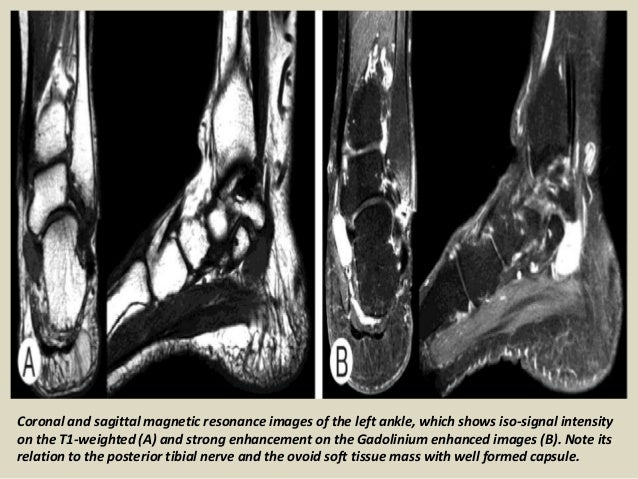
Its true incidence is unknown though it is an uncommon entrapment mononeuropathy. It is an entrapment syndrome of the entire tibial nerve behind the medial malleolus and under the flexor retinaculum or laciniate liga-. MRI is able to demonstrate a space-occupying lesion and its relationship to the posterior tibial nerve and its branches.
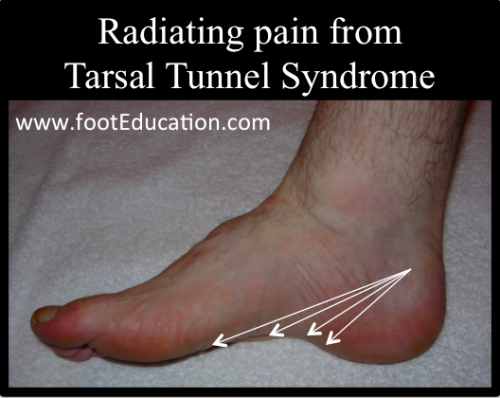
Classic or proximal tarsal tunnel syndrome is the entity to which many clinicians refer when the term tarsal tunnel is used. This information aids in surgical planning by determining the extent of the decompression required. Patients with TTS typically complain of numbness in the foot radiating to the big toe and the first 3 toes pain burning electrical sensations and tingling over the base of the foot and the heel.
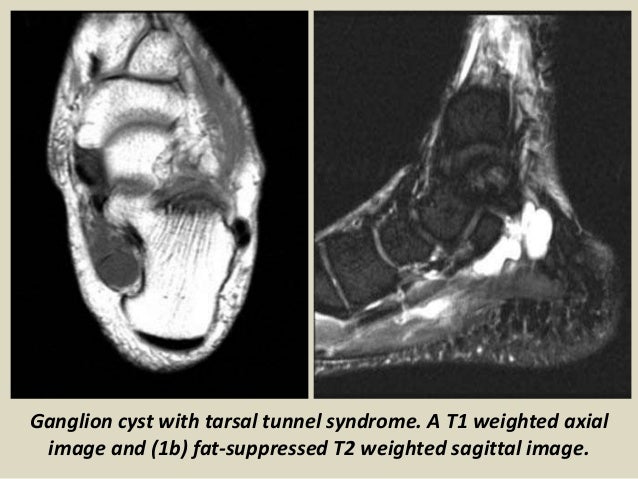
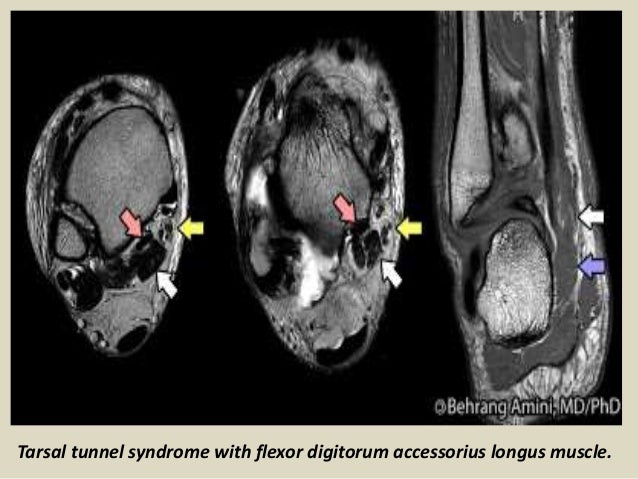
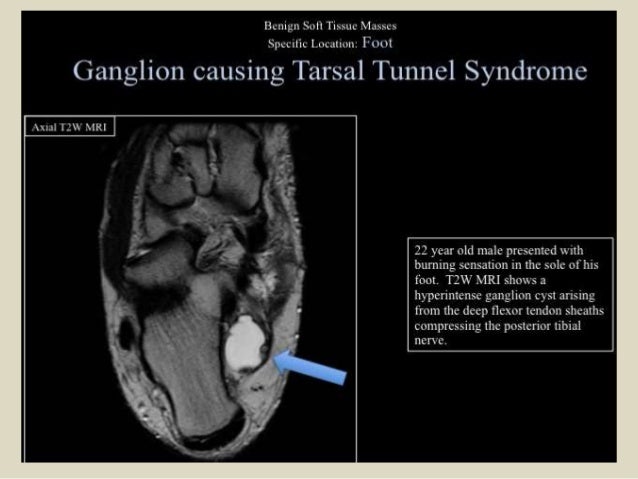
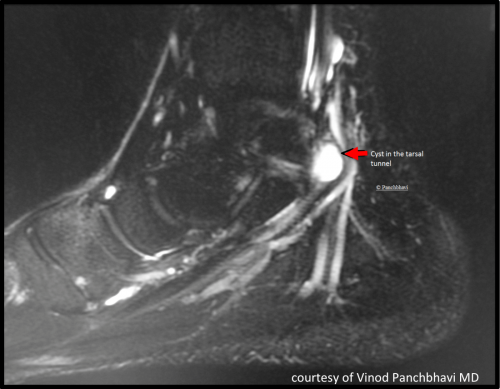
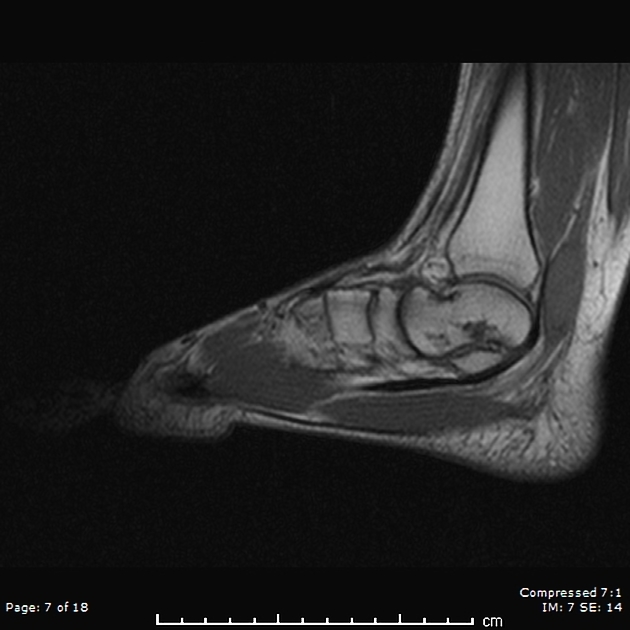
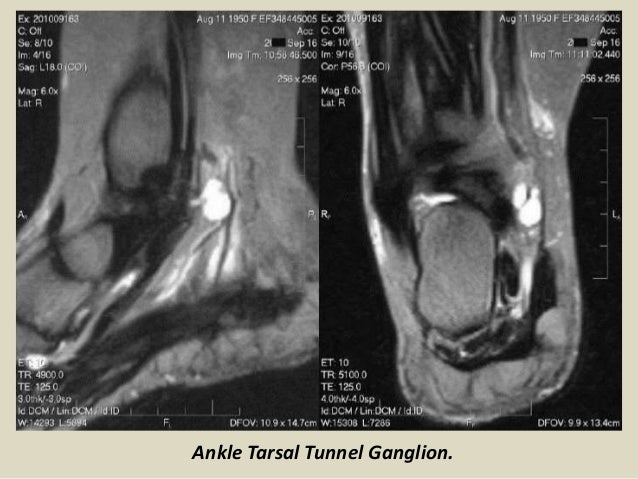
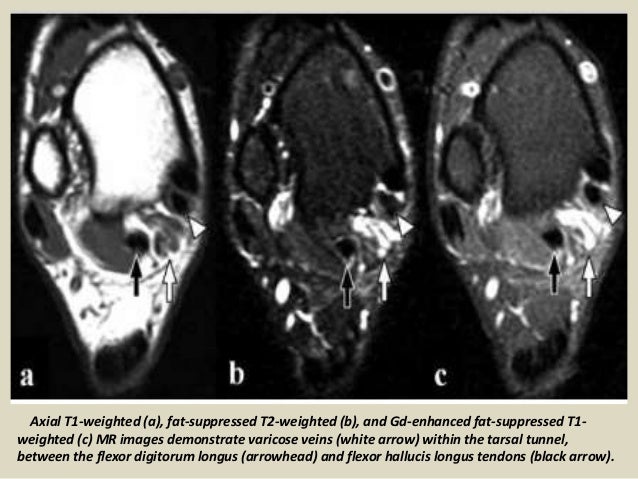
It was first described by Keck in 1962. MR imaging in tarsal tunnel syndrome Magnetic resonance imaging was used to demonstrate the normal anatomy of the tarsal tunnel in two volunteers and to evaluate 33 feet in 27 patients with tarsal tunnel syndrome. Posttraumatic fibrosis ganglion cyst tenosynovitis tumor of the nerves or other structures.
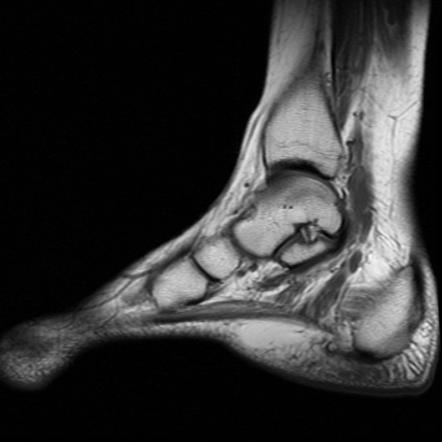
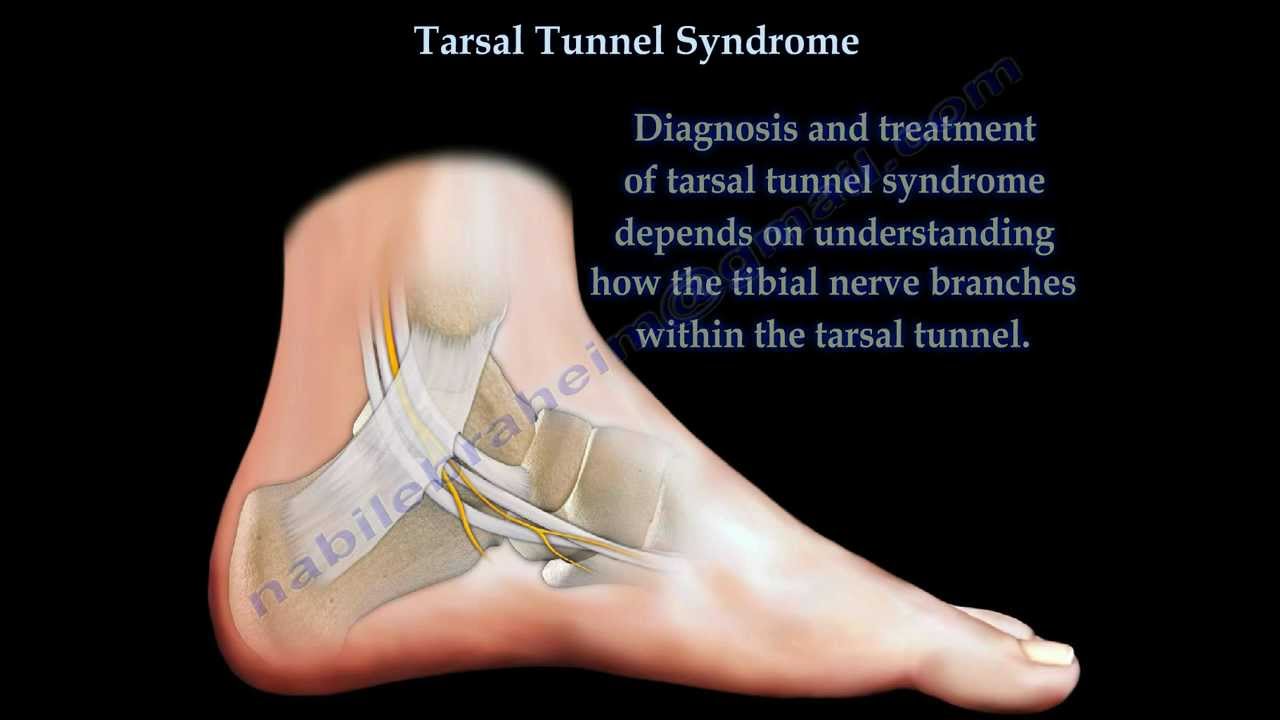
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a well-known but rare entrapment neuropathy involving the posterior tibial nerve in the tarsal tunnel a fibro-osseous channel extending from the medial aspect of the ankle to the midfoot.
MR imaging in tarsal tunnel syndrome Magnetic resonance imaging was used to demonstrate the normal anatomy of the tarsal tunnel in two volunteers and to evaluate 33 feet in 27 patients with tarsal tunnel syndrome.
In our small series MR imaging accurately showed the lesions responsible for tarsal tunnel syndrome. MRI is able to demonstrate a space-occupying lesion and its relationship to the posterior tibial nerve and its branches. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome MRI Test MRI is ideally suited for evaluation of the tarsal tunnel due to its excellent soft tissue contrast ability to demonstrate neurovascular and musculotendinous structures and sensitivity to soft tissue pathology. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. The tarsal tunnel is divided by fibrous septae joining the flexor retinaculum to the calcaneus forming four separate compartments - one for each of the tendons and one for the neurovascular bundle 1-3. Classic or proximal tarsal tunnel syndrome is the entity to which many clinicians refer when the term tarsal tunnel is used. It is an entrapment syndrome of the entire tibial nerve behind the medial malleolus and under the flexor retinaculum or laciniate liga-. MR imaging in tarsal tunnel syndrome Magnetic resonance imaging was used to demonstrate the normal anatomy of the tarsal tunnel in two volunteers and to evaluate 33 feet in 27 patients with tarsal tunnel syndrome. It was first described by Keck in 1962.
The tarsal tunnel is divided by fibrous septae joining the flexor retinaculum to the calcaneus forming four separate compartments - one for each of the tendons and one for the neurovascular bundle 1-3. Compression of tibial nerve within tarsal tunnel. Entrapment neuropathy of tibial nerve and its branches on medial aspect of ankle. Classic or proximal tarsal tunnel syndrome is the entity to which many clinicians refer when the term tarsal tunnel is used. It was first described by Keck in 1962. Patients with TTS typically complain of numbness in the foot radiating to the big toe and the first 3 toes pain burning electrical sensations and tingling over the base of the foot and the heel. Ab Axial T1WI a and spin-echo T2WI b demonstrate a lipoma arrowheads in the upper tarsal tunnel compressing the posterior tibial nerve arrows.




























Post a Comment for "Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Mri"